Industry Background: Why Green Printing Matters
In today’s era, where environmental protection and sustainable development are widely advocated, green development has become a global consensus. As a resource-intensive industry, the printing sector is entering a critical stage of transformation and upgrading.
Embracing environmental responsibility, improving resource efficiency, and promoting a circular economy are no longer optional. They have become essential directions for the sustainable development of printing-related enterprises worldwide.
Current Challenges Facing the Printing Industry
Although notable progress has been made in green printing practices across different regions, the industry as a whole still faces significant challenges. Many small and medium-sized printing enterprises continue to rely on traditional production methods and have yet to fully adapt to modern, environmentally responsible manufacturing models.
At the same time, companies are under increasing pressure from rising raw material costs, growing labor expenses, and continuous demands from customers for lower prices. Under this dual pressure of escalating costs and shrinking margins, maintaining sustainable growth has become increasingly difficult.
The Way Forward: Innovation and Intelligent Manufacturing
In this context, innovation is no longer a choice—it is a necessity. Forward-looking enterprises must actively pursue technological upgrades, process optimization, and the adoption of intelligent and automated equipment.
Only those companies that clearly identify the right direction and take proactive action can successfully transform and remain competitive amid economic uncertainty and market challenges.
Green printing is the road toward the future.
Our Solution: Supporting Plastic Reduction with Molded Pulp Technology
In response to global environmental policies aimed at reducing plastic waste, our company has developed advanced molded pulp equipment to support sustainable packaging production and help customers transition from plastic-based solutions to eco-friendly alternatives.

Product Overview
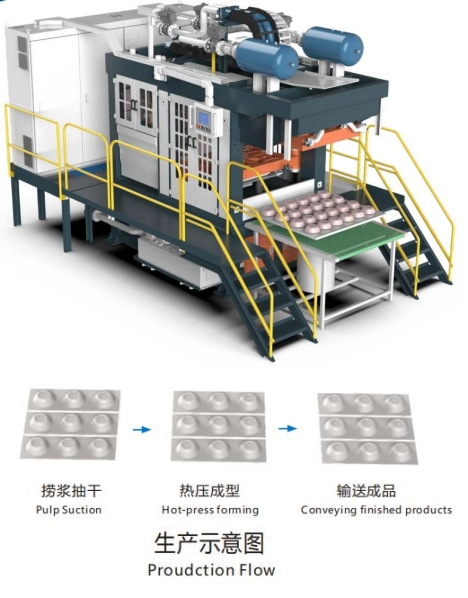
HM-ZX1080 Automatic Molded Pulp Tray Forming Machine
The HM-ZX1080 Automatic Molded Pulp Tray Forming Machine is a compact, two-stage pulp molding solution designed for efficient, flexible, and sustainable production. The machine supports fully automatic operation with single-machine or multi-machine configurations, quick mold changes, and stable performance.
It is particularly suitable for small to medium batch production and supports a minimum draft angle of 0 degrees, allowing greater flexibility in product design.
Key Structure and System Design
Stable Machine Structure
The main frame is manufactured from high-quality carbon steel and processed through welding and annealing to enhance overall stability and long-term durability.
High-Strength Hot Pressing System
The hot-pressing molds are made of nodular cast iron, ensuring excellent strength, rigidity, and reliability during continuous operation.
Stainless Steel Wet-End Components
All components in direct contact with wet pulp, including pulp tanks and conveying pipelines, are made of stainless steel to ensure corrosion resistance and hygiene.
Automation and Control System
The machine is equipped with a PLC and touch screen human-machine interface, enabling precise control of key production parameters such as suction time, hot-pressing time, and platform movement.
A positive and negative pressure control system supports smooth demolding of both semi-finished and finished products.
Cleaning, Transfer, and Heating Systems
-
High-pressure water spray cleans the mold surface
-
Low-pressure water spray removes rough edges
-
An automatic turning mechanism transfers products to the conveyor belt after hot pressing
-
Electric heating provides stable and controllable heat for forming and drying
Production Process Overview
Pulp Suction Section
The pulp is adsorbed onto the forming mold, pre-pressed, and then transferred to the hot pressing section.
Hot Pressing Section
The pre-pressed wet billet is transferred to the hot-pressing mold, where it is formed and dried under high temperature to achieve the final product shape.